|
What is no-load power waste?
No-load power waste is a
subset of standby power
waste. No-load power is the
energy used by a device when
it is disconnected from it's
load and performing no
function. For example, a
mobile phone charger that is
plugged into the wall, but
not connected to the phone
will still consume power.
Linear chargers can consume
between 0.8 W to 2 W even
when they are disconnected
from the phone.
Which devices use standby
power?
Almost any device with an external
power supply or (wallpack),
remote control, or clock
display will draw power
continuously. Literally every
electronic product that
plugs into the wall such as
TVs, VCRs, DVDs, washing
machines, cell phone
chargers, night lights,
cordless and feature phones,
refrigerators, cable TV
decoders, satellite TV
decoders, radios, computers,
printers, monitors, fax
machines, copiers, modems,
audio amplifiers, industrial
control units, motor
controls, etc. etc. It is
estimated that there are
approximately 3 to 4 billion
AC to DC power supplies
world wide every year. Sometimes
there is no obvious sign of
continuous power consumption
and you need a meter to be
certain
Why
are standby power losses a
problem?
While individual device
standby losses may seem
insignificant, when you
multiply the number of
households, by the number of
devices in a household and
the amount of time each
spends in standby, the
problem adds up quickly. It
is estimated by
International Energy Agency
that 5 to 15% of household
electricity consumption
worldwide is wasted in
standby mode. Altogether,
standby power use is roughly
responsible for 1% of global
CO2 emissions. In the US,
each watt of energy costs
approximately $1 to $1.5 per
year. The Lawrence Berkeley
National Lab estimates that
standby waste costs US
households over $5 Billion
in electricity a year.
According to the Department
of Energy, the amount of
standby energy used per year
in the US is equivalent to
26 average sized power
stations!
As the popularity of home
electronics and number of
new appliances with
electronic controls and
features increase, this
problem will continue to
grow.
How
can standby power
consumption be reduced?
Up to 90% of standby power
is wasted energy consumed by
inefficient power supply
designs and unnecessarily
energized components. The
Lawrence Berkeley National
Lab estimates that a 75%
reduction is possible in new
equipment and that nearly
all standby functions can be
performed with a total
appliance standby power of
one watt or less. This can
be achieved by using
improved power supply
technologies and designs,
namely, by replacing
inefficient linear power
supplies with smarter
switch-mode power supplies.
What’s wrong with the
current technology -- linear
power supplies?
Linear power supplies, also
referred to as "energy
vampires" because of their
energy-sucking nature, work
off of old technology from
the 1800's, which hasn't
kept pace with current
innovation. Linear
transformers use large iron
cores and require many turns
of copper wire in order to
convert regular 50/60 cycle
AC house current to the
safer low-voltage DC needed
to power our appliances and
electronic devices. As a
result, they are extremely
large and bulky, often times
covering two outlets on your
wall plate or power strip.
Moreover, linears do not
have the smarts to recognize
the standby or sleep mode of
the appliance and cut back
the consumption accordingly.
As a result they consume
many more watts than
necessary. As a test, go
feel one of the bulky
linears plugged into the
wall. It will be warm to the
touch...those are wasted
watts!
How
are switch-mode power
supplies better?
The second-generation power
supply, called the
switch-mode power supply or
"switcher" for short,
arrived in the late 1960s.
By increasing the AC
frequency from 50 or 60
cycles-per-second to several
thousand cycles-per-second,
engineers discovered they
could reduce the size and
weight of the transformer
and significantly improve
its efficiency (reduce the
amount of energy wasted in
the form of heat
dissipation).
Why
do inefficient linears still
exist?
Despite being bulky and
inefficient at converting
power, linears are popular
because they have become
very cheap to manufacture.
Until recently, under 5 W
switch-mode power supplies
haven't been competitive in
cost and since product
manufacturers don't have to
pay the electric bill, there
hasn't been an incentive to
prioritize energy efficient
designs. It's only been in
recent years that
governments and
environmental agencies have
started to develop standby
energy policies that reward,
or in some cases, mandate
energy efficient designs.
Hunting Energy Vampires
Look around
your house for external power
supplies – the AC adapters that
charge cell phones, cordless
phones, modems, computer
speakers, baby monitors, tools,
and many other devices. They
lurk in surprising numbers under
your desk, in your garage,
behind your TV set, and in your
kitchen. ENERGY STAR estimates
that the average household has
up to ten of these devices
plugged in all the time.
Some adapters
get warm to the touch, even if
they’re not charging a device.
These copper-and-iron
"energy vampires" are
continuously sucking electricity
from the wall and burning it off
as heat.
When shopping
for electronic products, look
for external power supplies that
are compact and
lightweight – chances
are they’ll remain cool to the
touch when plugged in. These
power supplies could save you $3
to $6 over the life of the
product and help make a dent in
greenhouse emissions.
Power supplies are also found
inside electronic products such
as DVD players, TVs, desktop
computers, and consumer
appliances.
According
to
Lawrence Berkeley National
Laboratory (LBNL), as much
as 10 percent of a typical
residential electric bill is
spent on “standby” power – the
power consumed while products
are turned “off” or otherwise
performing no useful function!
Most electronic products
continue to consume power unless
they are unplugged from the
wall. TVs, DVD players, CD
players and audio amplifiers
consume power all the time. Any
appliance with an LED display,
touchpad controls or a clock –
such as a microwave oven,
refrigerator or dishwasher – is
always on. Even a cell-phone
charger left plugged into the
wall consumes power, even when
not charging the phone.
Tips
for Minimizing Standby Power
Waste
- Don’t leave cell-phone
chargers and other battery
chargers plugged into the
wall when they’re not
charging anything. Any heat
coming from a power supply
indicates wasted watts.
- Consider unplugging
kitchen and office products
that are used infrequently.
For example, external
computer speakers are often
powered by wasteful adapters
that continuously draw
power, even though the
speakers may not be in use.
- When leaving home for an
extended period of time,
consider unplugging as many
electronic devices as
possible. TVs, DVD players,
audio equipment, cordless
phones and coffee makers can
cost you money if they're
plugged in while you're
gone.
Electricity Energy Monitors
The basic figures contained
within a monthly or quarterly
electricity bill do not give you
much information as to where
your electricity is going - they
just tell you how much you have
used in total during that period
and how much totally you need to
pay. Therefore it is well worth
considering purchasing an
electricity usage monitor and
using it to see exactly where
all your hard-earned money is
going.

One great way to find out how
much electricity each of your
household appliances and
electronic devices uses is with
a wireless electricity
power/energy monitor, which
shows you in real time exactly
how much money your total home
or office electricity usage is
costing you. These monitors can
help you reduce your electricity
consumption by as much as 20%
simply by showing you what you
are using.
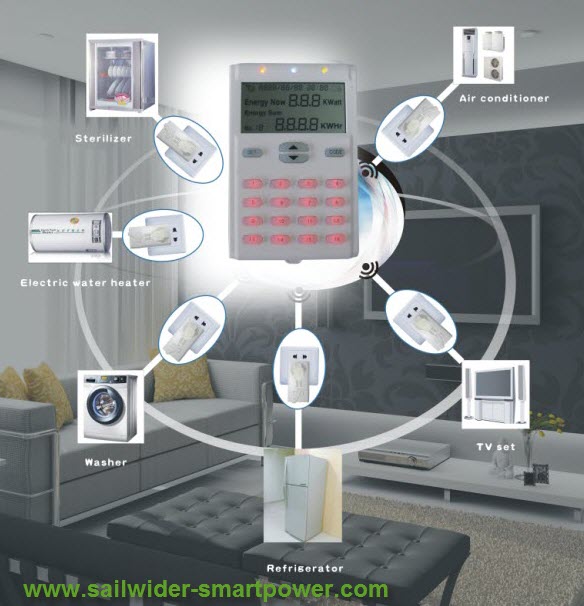
Sailwider-SmartPower is a developer and
manufacturer of electricity power
monitor and controlling system.

Most electricity energy monitors
in the market are uni-directional
(1-way) only, that means you can
only get energy consumption
information from the monitor.
The
bi-directional (2-way)
electricity power monitoring and
control system
from Sailwider-SmartPower makes
the user not only able to
monitor the electricity usage,
but also can easily remote
control the connected electrical
appliances wirelessly, providing
great convenience to electricity
efficiency management.
Electronics That Are Sucking
Electricity Even When Not In Use
Have you ever looked at your
electricity bill and wondered
“Huh, am i really using all this
electricity? I can’t believe
it!”? You may have not known
this, but you may only be
responsible for about 70% of
that electricity bill. The
remaining 30% could be all your
electric equipment sucking
electricity even when you are
not using them. The electricity
used by them when not in use is
probably only a small amount,
but the number of electronics
that we all buy and the fact
that they are connected to the
grid 24×7 adds up to a
substantial amount of electric
energy being wasted for nothing.
This energy wastage goes by
many different terms like
vampire power, phantom load and
standby power sucker.
Here are examples of some
common electronic equipment,
that we use in our daily lives,
wasting energy when not in use.
-
Television – The idiot
box is probably the
biggest culprit when it
comes to sucking
unnecessary power.
Almost all modern day
manufactured televisions
have a “standby” mode
where your TV is not
actually turned off. It
is just in a waiting
mode, so that when you
press on the remote it
will immediately come
back to life.
-
DVD players – Like TVs,
DVD players are also on
standby mode when
plugged in and not being
used. Most DVD players
will have a lit screen
displaying either the
time or the mode that it
currently is in.
-
Computers and Computer
Monitors – I hate it
when i am driving on the
road and can see
computer screens in
buildings displaying
screen savers. Why cant
people just turn off
their computers and
computer monitors when
not being used? Are you
unplugging your laptop
after you turn it off?
Laptops will continue to
charge their batteries
even after they are
turned off but when
still plugged in. Make
sure you are switching
off your computer
monitor after you turn
off the computer
otherwise the monitor
just goes to a standby
mode.
-
Cell Phone Chargers and
Power Adapters – Your
cell phone charger and
power adapters (like for
laptops) are using power
even when they do not
have a device plugged
into them. So if you are
not charging your cell
phone or using a device
that needs the power
adapter, just unplug
them.
-
Microwaves – They make
our lives so much easier
by heating up our food
in minutes. They display
time on a digital
display and usually have
a lighted screen. The
screen is lighted and
time displayed even when
you are not using the
microwave oven. This is
unnecessary and a total
waste of electricity.
How many clocks does one
need in a house?
-
Stoves – Like
microwaves, stoves also
have a digital display
and a lighted screen
that is using
electricity even when
the stove is not turned
on.
-
Hand-held vacuum
cleaners – The constant
charging of hand held
vacuum cleaners is also
using electricity. Even
though they are handy
and ready to use when
you need them, the
constant charging takes
up a substantial bit of
electricity.
Steps
you can take to stop/reduce
unnecessary sucking of
electricity
The most easiest solution to
save money and stop unnecessary
usage of electricity would be to
unplug devices and equipments
that are not being used. Plug
them into an electric outlet
only when need be. Using of
power strips is a good idea for
TVs, DVRs and DVD players as
they are all probably being used
at the same time. You can turn
off one switch that controls the
power strip and in turn
automatically control power to
each of those devices.
Also, remember to unplug all
these devices and especially the
stoves and microwaves when you
are on a holiday or out for an
extended period of time. |



